Our “Electricity for Kids” guide is a fun, informative read for K-12 students. Learn all about electricity, how it’s generated, a timeline of discovery, lightning safety, and more!
Table of Contents
-
What is Electricity?
-
Quick Facts on Electricity
-
How is Electricity Made?
-
Non-Renewable Resources
-
Nuclear Power (New Page)
-
Coal Power (New Page)
-
Natural Gas (New Page)
-
-
Renewable Resources
-
Sun (Solar)
-
Wind
-
Water (Hydro)
-
Biomass
-
Geothermal
-
-
-
Lightning (Types, Safety, and Myths)
-
History of Electricity (Timeline)
-
How Does Electricity Get Into Our Homes?
-
Electricity Vocabulary Terms
What is Electricity?

E ? lec ? tric-i-ty (noun)
Electricity is a type of energy that comes from the flow of electrical power, also known as a charge. Electricity is used to power our homes, lights and electronics. We get electricity from sources like coal, energy, natural gas and oil.
Electricity is a secondary source of energy, which means it must be made from these items. We have learned how to take items that we find in nature or products like oil and transform them into the electricity we need to power our homes. Pretty neat, right?
We use electricity every single day in our lives. Most of us don?t even realize how much we use electricity every day. Electricity may be common in our everyday lives, but it doesn?t mean that electricity is simple or easy to create.
Electricity is complicated and powerful, and it is an important part of our lives. Take a minute to learn more about electricity, you may be surprised by some of the fun facts behind the world?s most amazing source of power.
← Back to the Table of Contents
Quick Facts on Electricity
1. Electricity is so fast that it travels at the speed of light. That is 186,000 miles per second.
2. Electricity can be made from all types of things. We can use water, the sun, wind and even animal droppings to make electricity.
3. Lightning is actually a type of electric energy found in nature.
4. Electricity is the most common type of energy.
5. If you took 25,000 fireflies and put them together, they would make as much electricity as a single 60 watt incandescent light bulb.
6. Coal is the most common way to make energy. It takes 440 million years just to make coal.
7. Solar power is one of the most popular natural sources of electricity. The sun is so powerful at making energy that in just one hour it could make enough energy for the whole world to use for a whole year.
8. Electric eels really are electric. They can make a surge of electricity that is stronger than the power you get from the outlet in your house.
9. Your air conditioner uses 10 times as much electricity than a fan does. When you can, try to use your room?s fan instead of blasting the AC, it will save you and your family a lot of electricity.
10. Your refrigerator typically uses more electricity than any other appliance in your home.
← Back to the Table of Contents
How Is Electricity Made?
Electricity is such an important part of our lives… but how is it made? Where does it comes from? There is no one answer! Electricity can be made from a number of different resources. There are both renewable (natural) and non-renewable sources.
← Back to the Table of Contents
Non-Renewable Resources
Non-renewable resources are items like coal and natural gas. We can use them to create power, but when we use them they create waste. Eventually, these resources will run out.

Here are the main types of renewable resources.
- Nuclear Power
- Coal (Fossil Fuel)
- Natural Gas
Here is how they work:
1. These non-renewable resources are burned or used in order to make heat.
2. This heat converts water into steam.
3. This steam then turns an engine within the power plant, also known as a turbine.
4. When the turbine starts to spin it creates friction which makes electricity!
← Back to the Table of Contents
Renewable Resources
Then there are renewable resources. These are things found in nature that we can use over and over again to make electricity and they never run out and they don?t make any waste!

The most common types of renewable resources are:
- Sun (Solar)
- Wind
- Water (Hydro)
- Biomass
- Geothermal Power
And here is how they work:
Solar Power
We take energy directly from the sun and use its light and heat. The most common way to do this is with big solar panels. They capture the sun?s light and turn it right into electricity. You can also use the sun?s head to create steam that spins turbines and generates electricity.
Wind Power
Have you ever seen those big windmills on the side of the road? They are used to make electricity. When the wind makes these mills move it makes energy that we can then collect and turn into electricity.
Water Power (Hydro Power)
When water falls over a waterfall, down the current of a river or through a dam, it can be collected in something called a turbine. These turbines have big blades in them and when they spin, they generate power we can turn into electricity.
Geothermal Power
There center of the earth is very hot, just like a volcano. Did you know we can use this heat to create electricity? We can take the heat and make it into steam in power plants that will generate power.
Biomass
Biomass is a term used to describe wood, plants, crops and even animal droppings. These natural items can be used instead of coal or natural gas. We can burn this waste to power turbines and create electricity.
← Back to the Table of Contents
Lightning
Lightning is a form of electricity found in nature. You might see lightning during a thunderstorm, when thick black storm clouds are in the sky. This is happens when the storm clouds form two layers. The space between these two layers get electrically charged, until a spark generates in the atmosphere, or between the ground and the atmosphere. When lightning hits the ground, this is called a lightning strike.
There are many different types of lightning. While some do not hit the ground, all conduct electricity. Below are only a few examples.
Anvil Crawler
This kind of lightning goes from cloud-to-cloud across the sky. You can usually see this type of lightening from a great distance.
Dry Lightning
This kind of lightning happens when there is very little, or no rain. It is the most common cause of wildfires in places like, Canada, Australia and the United States.
Forked Lightning
This type of lightning looks like a tree branch or a forked road. It shoots from the sky all the way to the ground.
Rocket Lightning
This lightning happens at the bottom of a cloud. It shoots out in a straight line, just like a rocket!
Super Bolt
This type of lightening is one hundred times brighter than any other kind of lightning. It is very rare ? only one in a million lightening strikes are a super bolt.
Because lightning is a form of electricity, it is also very dangerous. While it looks beautiful from a distance, lightning bolts are hotter than the surface of the sun! Lightning can light up a thundercloud, stretch between clouds or even strike the ground.
Sometimes these lightening strikes can hit trees, buildings, and people. To make sure you stay safe, it is very important to know what to do in a lightening storm.
Lightning Safety
When you see lightning, the best place to be is inside your house or a building. Even if you can’t see thunder — as the National Weather Service says, “If thunder roars, head indoors” — you can still be struck by lightning. Once inside, wait for the storm to pass. Another good place to go is inside a car ? but make sure the windows are closed!
If you are outside, there are many things you can do to get to a safe place. Check out the following tips to learn more.
It?s getting dark out there…
While you are outside, it is important to keep an eye on the sky. If the sky starts to get dark when the sun should be shining, storm clouds might be rolling in! If you still aren?t sure about the weather, try asking yourself these questions:
- Are the clouds really dark?
- Is the wind getting stronger?
- Do I hear thunder rumbling?
- Is it raining?
If you see it…
If you answer ?yes!? to any of those questions, it?s a good idea to head inside your house, a sturdy building, or car. Don?t wait! Leave right away. If you can, run home or to a friend?s house. If an adult is nearby, go to them for help.
When you are inside, there are some things you can do to make sure you stay safe. Don?t use devices that need electricity like, a computer or other appliances. It’s best to turn them off.
Sometimes lightning can hit power lines and cause a loud explosion. If you have a corded telephone, don’t use it. The noise can be deafening!
You should also wait until the storm passes to take a shower or use any water. Lightning can travel through water and give you quite a shock.
Remember…
Lightning is electricity, which means that some objects on the ground attract or conduct lightning. It?s a very good idea to stay far away from these objects so that you don?t get hurt. These objects include:
- Bleachers
- Sheds
- Picnic areas
- Bodies of Water
- Water
- Puddles
- Metal
- Trees
If you ever see anyone get struck by lighting, call 9-1-1 right away. They will need medical attention.
Lightning Myths
#1 ? I can finish playing my game before I go inside.
If you see any signs of a lightning storm, you should head home right away. Do not finish your game and do not wait for it to start raining. It is important to try to get to a safe place right away.
#2 ? Lightning never strikes the same place twice.
If there is a tall structure or object, lightning can hit it more than once. Buildings like the Empire State building can get hit over 100 times every year!
#3 ? Only tall objects and buildings get hit by lightning.
While it might seem like only tall objects get hit by lightning, this isn?t always true. Scientist can?t really explain why lightening hits certain things and not others. It is true that something tall is more likely to get hit by lightning, but not always!
#4 Lightning doesn’t generate energy.
When lightning strikes, the electricity doesn’t get used to power buildings or houses. Most of it goes into the ground. However, there are scientists working on different ways to try and harvest electricity from lightning. This will help to create new energy without harming the environment.
← Back to the Table of Contents
History of Electricity (Timeline)
It may seem as though electricity has been around forever, but in reality electricity has only been here for a few hundred years. No one person “invented” electricity, but Benjamin Franklin is often given the title of official ?founder? of electricity.
He’s not alone in making electricity what it is today:
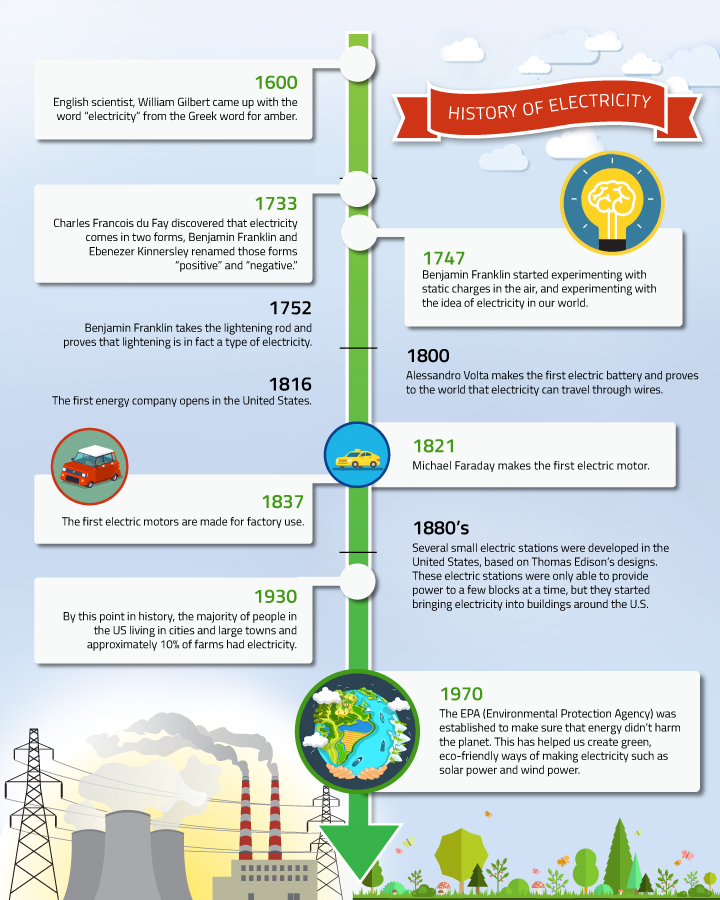
1600 – English scientist, William Gilbert came up with the word ?electricity? from the Greek word for amber.
1733 – Charles Francois du Fay discovered that electricity comes in two forms, Benjamin Franklin and Ebenezer Kinnersley renamed those forms ?positive? and ?negative.?
1747 – Benjamin Franklin started experimenting with static charges in the air, and experimenting with the idea of electricity in our world.
1752 – Benjamin Franklin takes the lightening rod and proves that lightening is in fact a type of electricity.
1800 – Alessandro Volta makes the first electric battery and proves to the world that electricity can travel through wires.
1816 – The first energy company opens in the United States.
1821 – Michael Faraday makes the first electric motor.
1837 – The first electric motors are made for factory use.
1880s – Several small electric stations were developed in the United States, based on Thomas Edison?s designs. These electric stations were only able to provide power to a few blocks at a time, but they started bringing electricity into buildings around the U.S.
1930 – By this point in history, the majority of people in the US living in cities and large towns and approximately 10% of farms had electricity.
1970 – The EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) was established to make sure that energy didn?t harm the planet. This has helped us create green, eco-friendly ways of making electricity such as solar power and wind power.
← Back to the Table of Contents
How Does Electricity Get Into Our Homes?
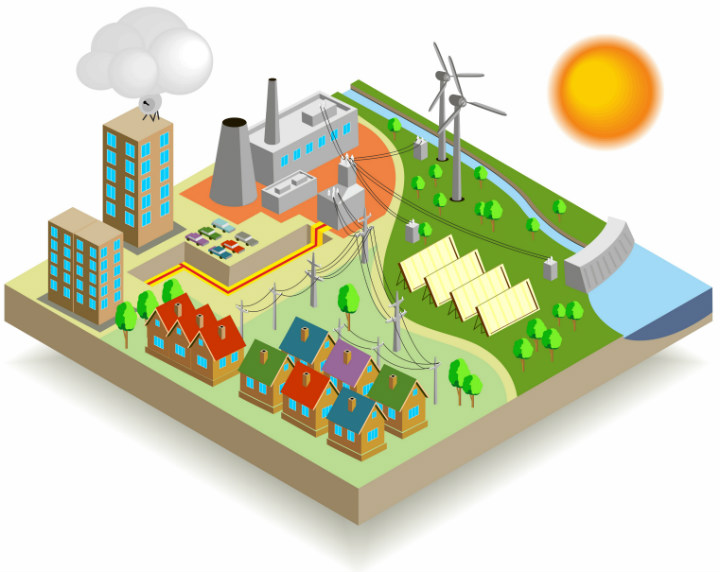

When we need electricity, all we really need to do is flip a switch or turn the button on our television, and we can instantly start using as much power we need. It?s almost like magic. It seems so easy for electricity to get into our homes, when the truth is electricity has to travel hundreds of miles in order for us to use all of our favorite electronics.
So how does electricity get into our homes?
You know those poles and wires you see along the road? Those are the ?roadways? for electricity to travel on. These wires and poles are very important and help make it possible, but before electricity can start traveling to our televisions and microwaves, it needs to be made first!
Here is how it works:
1. Electricity is made at huge power plants across the country. These factories can use coal, wind, water, natural gas and other resources to make electricity.
2. Once the plant has made the electricity it is sent through things called transformers. These transformers give the electricity the boost it needs to travel long distances. Usually electricity has to travel hundreds of miles.
3. This electrical charge is pushed into lines called transmission lines. These are the big wires you see all over your community. These lines stretch through the country so everyone can have access to electricity.
4. After that charge has traveled miles and miles through the transmission lines it arrives to the substation. Here, the charge is slowed down a bit so it isn?t so powerful, now that it doesn?t have to travel much farther. The boost it got from the transformers is taken away so it can safely travel to your home.
5. This electricity then goes through smaller lines called distribution lines. These distribution lines are connected to our homes, schools and buildings throughout our neighborhood.
6. These distribution lines bring the electricity through the meter outside your house. This meter tells you how much you and your family uses in electricity every month. From there that burst of electricity goes through all these little wires inside the walls of your home and to the outlets and switches all over your house, so you can start using electricity however you want.
When you plug in an electronic to one of these outlets, that electricity that started in a plant hundreds of miles away is pushed right through your item, allowing you to use your favorite gadgets whenever you want.
← Back to the Table of Contents
Electricity Vocabulary Terms
There are so many different terms that help us understand electricity and how it works. The more vocab words you know about electricity, the more you know about the energy you use every day.
A
Amps – Amps are used to measure the flow of an electric current through a substance or material (also known as a conductor).
B
Battery – A cell or a group of cells that can create an electric current.
Blackout – When an entire area supplied by the same electric company loses power. When the lights go out during a storm, this is typically called a blackout.
C
Circuit – A path that an electric current follows in order to reach its final destination. For example, when a burst of electricity goes from the meter in your house to the computer in your room, it is following a circuit.
Conductor – Any type of material that allows electricity to flow through it.
Current – The flow of electricity.
F
Fuse – A very important safety device that stops the flow of electricity in situations where too much electricity could be dangerous. Sometimes when you are using an item at too high of power, such as a hairdryer, it may cause your entire outlet to turn off. Your parents may refer to this as ?blowing a fuse.? This is happening because there was too much electricity going through the socket in your home and the fuse helped keep you safe.
G
Generator – A machine that is put into motion to create electricity.
Geothermal Energy – Energy that is taken from the heat from underneath the earth.
Grid – A grid is a series of paths, substations and power lines that allow electricity to travel from one place to another.
H
Hydro Power – Electricity that comes from running water.
I
Insulator – An item that does not allow electricity to run through it. Certain items may be insulated to keep electricity where it is supposed to be.
K
Kilowatt (KW) – A kilowatt is 1,000 watts. This is a common way of measuring how much energy something uses.
Kilowatt Hour (kWh) – Using 1,000 watts of electricity for a full hour. If your laptop uses 5 kWh it means it uses 5,000 watts of electricity every hour.
M
Megawatt – One million watts of energy or 1,000 kilowatts.
Meter – A machine that measures how much energy something uses. There is an electric meter outside your house that tells you how much electricity your family is using.
N
Nuclear Power – Energy that comes from a nuclear reactor. In these power plants, machines split atoms as a way to create electricity.
S
Socket – An opening in your home where you can plug electronics into is known as an electric socket. This is how you connect your devices to the electricity running through your home.
Solar Energy – Electricity that comes from the sun?s heat or light. This is a renewable source of electricity.
Solar Panel – A solar panel is a large device that captures the heat and light from the sun and turns it into usable energy for our homes and other buildings.
T
Turbine – A machine that takes moving energy, such as water, wind or steam and powers a generator that allows that moving energy to turn into electricity.
V
Volt – A volt is a way to measure how much force an electric current has when it moves through an object, or a conductor.
W
Watt – The main way we measure electrical power. 1,000 watts= 1 kilowatt. 1,000,00 watts= 1 Megawatt.
Wind Power – Electricity that comes from wind. This is a renewable source of energy.
Wind Turbine – A big windmill type structure that captures the power and energy of the mind and uses the movement from the wind to power a generator. This generator then turns the wind?s movement into electricity.


